What is Identity Security?
Identity Security is the discipline of protecting digital identities—human and non-human—from unauthorized access, abuse, and compromise. It ensures that only the right people (or machines) get access to the right resources at the right time, and for the right reasons.
Unlike traditional identity and access management (IAM), which focuses on provisioning, authorization, and entitlements, identity security is proactive. It detects threats, enforces least privilege, prevents lateral movement, and fortifies every corner of your infrastructure. Think of IAM as your identity infrastructure and identity security as the protective layer securing your identity infrastructure and the identities within.
Welcome to your definitive guide to Identity Security—a fast-evolving field that’s reshaping how organizations protect their most critical asset: identity. Whether you’re a CISO, security analyst, or just curious about how the digital world keeps its gates locked (and who holds the keys), this glossary will take you from the fundamentals to futuristic best practices.
Why does identity security matter?
In a world where identities are the new perimeter, securing them is mission critical. Identities and IAM infrastructure need protection just like cloud infrastructure, endpoints, or networks.
Identity-first attacks continue to be the weapon of choice for cyber-attackers. Traditionally, organizations attempt to solve this challenge with a patchwork network of controls and tools, but the tools are outdated, or are simply another management solution, not security. This approach leaves gaps & blind spots that go unprotected, leaving systems vulnerable to attack.
Identity security is equally important to endpoint security or cloud security, which is why this category is extremely fast-moving and being rapidly adopted. According to the 2024 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, identity was the most implicated cause in reported breaches over the past year. Identity security exists to tackle this challenge.
As organizations evolve beyond traditional networks to cloud-based infrastructures, SaaS applications, and hybrid working environments, identities have been given unprecedented levels of power. They consist of employees, third parties, and machines all freely navigating on-prem applications and resources to cloud infrastructures and SaaS applications, all from different devices and endpoints around the world. This is great news for organizations in search of flexibility and efficiency—but not so much for security teams responsible for protection, governance, and compliance.
Today’s attackers are focused on identities. They’re stealing credentials, compromising legitimate accounts, and quietly navigating through environments to reach sensitive data. The problem? It’s harder than ever for organizations to maintain a clear view of who (or what) has access to what—and whether that access is appropriate or secure.
Without identity security, your infrastructure is only as strong as its weakest login.
Real-world impact: identity security in action
| Scenario | With Identity Security | Without Identity Security |
|---|---|---|
| Compromised admin account | Blocked with MFA + real-time enforcement | Potential domain takeover |
| Shadow service account | Detected and removed automatically | Credential theft + lateral movement |
| Zero Trust strategy | Enforced across all environments | Policy gaps + privilege creep |
| Regulatory audit | Automated evidence and reporting | Manual chaos and noncompliance |
Who and what does identity security secure?
Attackers don’t discriminate, and neither should your identity security. Every identity, regardless of type or privilege level, must be secured wherever they function in your estate, no matter what they’re doing. Identity security doesn’t end with individual identities: it’s about protecting your resources and environments too.
| Identities | Why it matters |
|---|---|
| Human users | Your workforce, your first line of risk |
| Non-human identities | Service accounts, APIs, bots—often overlooked, heavily privileged |
| Privileged users | High value targets for attackers |
| Third parties | Vendors, contractors—risky by default |
| AI agents | Fast-acting, highly connected, and vulnerable |
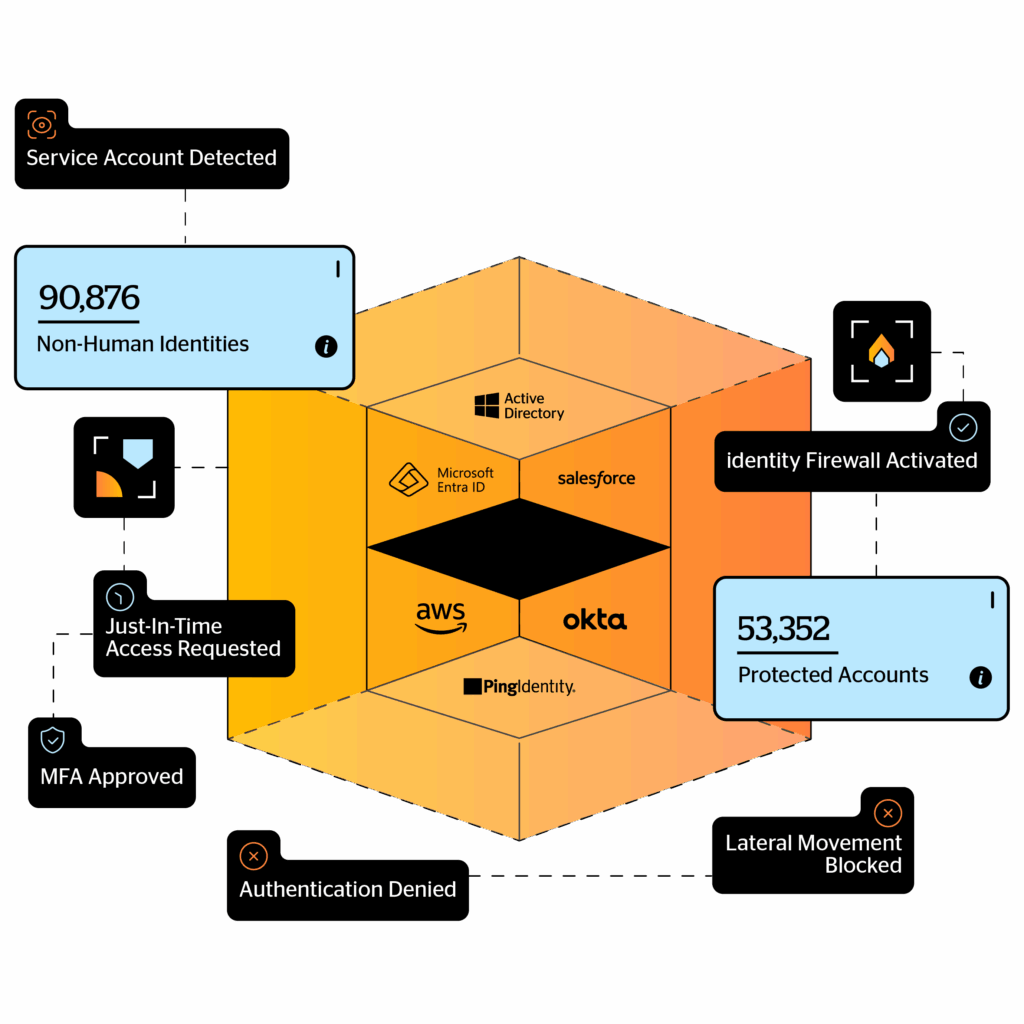
Environments that must be covered by identity security include on-prem, cloud and multi-cloud, hybrid, and OT (Operational Technology), while resources range from command-line tools to modern cloud workloads, SaaS app, and legacy systems. As more and more companies design hybrid and on-prem environment, it becomes even more important for them to move away from a patchwork of identity tools and security controls, to a holistic identity security solution that acts as a security layer for your identity fabric.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) vs. Identity Security: What’s the difference?
IAM provides the foundation—Identity Security enhances and enforces it. Said another way, IAM is the infrastructure plane, and identity security is the control.
IAM primarily focuses on provisioning, managing, and de-provisioning user identities and access permissions. It is essential for operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and reducing administrative overhead.
Identity security complements IAM by addressing the security gaps that IAM solutions often leave open. While IAM provides the foundational framework for managing identities and access, identity security ensures that these identities are protected from sophisticated cyber threats, such as credential theft, privilege escalation, and lateral movement.
For a comprehensive security posture, organizations should integrate IAM with identity security measures. This integration provides a holistic approach to managing and securing identities, combining the strengths of IAM’s access management with the proactive threat detection and response capabilities of identity security. An integrated approach like this helps organizations achieve robust protection against identity-based attacks while maintaining operational efficiency and compliance. Core elements of IAM include authentication, authorization, auditing, logging and monitoring, and elements of privileged access management.
Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying that users are who they claim to be. Strong authentication mechanisms are essential to prevent unauthorized access. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a widely used method that requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a resource. These factors can include something the user knows (a password), something the user has (a security token), and something the user is (biometric verification). Authentication is often a key part of IAM solutions, however in some cases, advanced authentication tools that can protect legacy resources can be found in an identity security product. As such, authentication can sit in both the infrastructure and security layer.
Authorization
Authorization determines what an authenticated user is allowed to do. It involves setting and enforcing permissions and access controls based on the user’s role within the organization. Role-based access control (RBAC) is a common approach, assigning permissions to users based on their roles, which helps ensure that users have the minimum necessary access to perform their duties.
Privilege management
Privilege management focuses on controlling and monitoring elevated access rights to minimize risks associated with privileged accounts. This includes attempting to implement the principle of least privilege, where users are granted the minimum levels of access—or permissions—needed to perform their job functions. Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions help manage and audit the use of privileged accounts, reducing the risk of misuse or compromise. PAM is typically considered part of both the infrastructure and security layer because it puts policy controls around privileged access and accounts. However, as organizations have evolved, the market has identified it needs to not just manage privileged access but to secure it. The market is also demanding easier ways to deploy privileged access security because legacy solutions are lengthy, time-consuming and often don’t end up delivering results.
Audit, Logging and Monitoring
Continuous audit, logging, and monitoring are vital for maintaining security and compliance. These activities involve tracking access and identity-related activities across systems to detect suspicious behavior, ensure policy compliance, and provide forensic evidence in the event of a security incident. Effective monitoring can help organizations identify and respond to potential threats in real time, thereby reducing the impact of security breaches.
IAM infrastructure is the foundational identity management and basic access controls that identity security sits above and enhances. While IAM infrastructure incorporates some basic security features, like MFA, identity security provides a complete security layer that protects against unauthorized access, misuse of privileges, and identity-based attacks. With a seamless integration between these two complementary elements of enterprise identity, organizations can significantly reduce their attack surface and enhance their overall security posture.
| Feature | Identity & Access Management (IAM) | Identity Security |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Authentication & provisioning | Inline threat prevention & enforcement |
| Visibility | Limited to managed systems | Continuous across all environments |
| Enforcement | Passive and limited | Real-time, risk-aware |
| Coverage | Human identities | Human + non-human identities, including service accounts |
| Threat Detection | Minimal | Built-in, proactive |
| Compliance reporting | Manual | Automated, real-time |
Critical real-world Identity Security use cases
Use case #1: Protect privileged access
Replace vaulting with JIT access, tiering, and policy enforcement.
Traditional privilege management – centered on vaulting and password rotation – fails to provide real-time visibility and enforcement, leaving organizations exposed. Further, legacy PAM solutions leave blind spots and are difficult to deploy, making it difficult to protect privileged identities in a timely and holistic manner.
Simply managing privileged accounts is not enough – concrete security controls must be in place to prevent privilege sprawl and unauthorized access.
With identity security, protecting privileged access should look like:
- Automatically discovering and classifying all privileged accounts into different tiers based on actual usage
- Applying Just-In-Time (JIT) access to domain privileged accounts with a single click to eliminate privileges with no expiration
- Enforcing least privilege policies with virtual fencing to prevent unauthorized privilege escalation
- Eliminating dependency on vaulting and password rotation
Use case #2: Stop lateral movement before it starts
Use MFA on command-line interfaces, detect in real time, contain attacks instantly.
Compromised credentials often lead to escalated privileges, reaching business-critical assets. Traditional detection and response capabilities lack visibility into all identities everywhere (from on-prem to the cloud, from human to NHI), allowing threats to spread undetected. To prevent breaches from escalating, organizations must stop unauthorized access before attackers embed themselves deeper and deeper.
With identity security, stopping lateral movement looks like:
- Enforcing MFA on all access interfaces, including legacy systems, airgapped networks, IT/OT, and command-line interfaces such as PowerShell, PsExec, and WMI
- Implementing real-time attack containment detection capabilities to block malicious attempts instantly and isolate compromised accounts before privilege escalation can occur
- Utilizing AI to continuously analyze authentication attempts and identify anomalies, enabling proactive credential misuse prevention
- Integrating identity-first incident response to halt attacks immediately, without manual intervention
Use case #3: Apply Zero Trust
Enforce dynamic, risk-based access everywhere—cloud, SaaS, and on-prem.
Identity is still the weakest link for many organizations, but traditional security tools struggle to enforce least privilege access across hybrid environments. Without universal enforcement and adaptive controls, organizations risk identity-driven breaches that undermine zero trust principles.
With identity security, applying zero trust looks like:
- Extending zero trust to every identity by enforcing least-privilege access policies for all human and non-human identities, eliminating standing privileges
- Enforcing Just-In-Time (JIT) access enabling dynamic, time-bound access approvals to reduce exposure without disrupting workflows
- Continuously authenticating and monitoring access by verifying every access request with risk-based, adaptive controls that automatically adjust to evolving threats
- Unifying zero trust across all environments to secure access across cloud, SaaS, and on-prem resources—all without requiring complex integrations or additional agents
Use case #4: Secure AD service accounts
Auto-discover, monitor, and protect NHIs without disrupting workflows.
AD service accounts often have elevated privileges, static credentials, and lack of direct oversight, making them a prime target for attackers. Without comprehensive visibility and control, these NHIs become an unchecked security risk, enabling credential theft and lateral movement.
With identity security, protecting AD service accounts looks like:
- Automatically discovering and continuously monitoring all service accounts across Active Directory, including unmanaged and orphaned accounts
- Enforcing least privilege access with adaptive Zero Trust policies to block unauthorized authentication attempts and prevent lateral movement
- Securing service accounts at scale without relying on disruptive password resets, ensuring protection without operational downtime
- Analyzing authentication patterns to detect and block suspicious service account activity in real time
Use case #5: Map the identity attack surface
Uncover shadow admins, legacy protocols, and misconfigurations.
Misconfigurations, legacy protocols, and excessive privileges open organizations up to risks like lateral movement and privilege escalation. Without proactive identity security posture management (ISPM), it becomes impossible to analyze and prioritize the most critical threats based on exploitation probability and impact-based scoring.
With identity security, mapping the identity attack surface looks like:
- Automatically identifying vulnerabilities such as legacy authentication protocols, shadow admin accounts, and misconfigured domain settings that create security risks
- Continuously monitoring and hardening Active Directory, cloud IdPs, and federated authentication systems to strengthen resilience against identity threats
- Improving identity hygiene by detecting and resolving operational issues, including excessive failed authentications and improperly synced cloud accounts
- Automating remediation efforts, reducing manual security work and ensuring rapid mitigation of identity-based threats
Use case #6: Maintain regulatory compliance
Demonstrate control, enforce policies, and automate audit reporting.
Proving identity security effectiveness to auditors and regulators can be a manual, time-consuming process. Traditional identity tools lack real-time enforcement, automated reporting, and full visibility across all identities, rendering audits complex and inefficient. Without a streamlined approach, organizations struggle to meet the evolving compliance mandates while maintaining strong security controls.
With identity security, compliance readiness looks like:
- Automating enforcement of identity security controls, including MFA, least-privilege access, and service account protection, to meet regulatory standards
- Ongoing monitoring of identity security posture and real-time reporting that provide auditors with clear evidence of compliance
- Applying adaptive policies that ensures privileged and service accounts meet PAM and identity protection requirements without disrupting operations
- Eliminating security gaps in authentication processes, ensuring compliance with frameworks such as NIST, HIPAA, and GDPR
Key Identity Security capabilities & solutions
| Product | What It Is | Why It Matters | What It Does |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR) | Detects and responds to identity-based threats in real time | Stops attacks at the identity layer | Blocks lateral movement, identifies compromised accounts |
| Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM) | Continuously assesses identity risks and weaknesses | Prevents misconfigurations & privilege sprawl | Provides risk scoring & remediation |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Second layer of identity verification | Prevents unauthorized access | Protects access points with low friction |
| Privileged Access Security (PAS) | Modern evolution of PAM that moves from managing privileged users to securing them | Protects the most sensitive identities | Just-in-time access, tiering, virtual fencing |
| Authentication Firewall | Identity-layer security for all authentication traffic | Applies Zero Trust at every interface | Blocks risky attempts at the source |
| AI Agent Security | Secures autonomous agents | New, growing threat surface | Applies policy enforcement to AI-driven workflows |
| Non-Human Identity Security | Protects service accounts, APIs, bots | NHIs outnumber humans 50:1—and are growing exponentially | Continuous discovery, adaptive access control |
Pro Tip: Ideally, your identity security should do ALL of this from a single platform.
Identity Threat Detection & Response (ITDR)
Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR) solutions focus on the detection and response to identity-based threats, providing security teams with the tools they need to efficiently monitor, identify, and mitigate attacks targeting user identities.
ITDR encompasses a range of technologies and processes aimed at continuously monitoring identity activities, analyzing risks, and responding to malicious activities in real time. ITDR is specifically designed to detect and counteract identity-based threats by providing advanced threat detection mechanisms that can identify and respond to identity misuse, credential theft, and privilege escalation.
Key benefits of ITDR
- Continuous threat detection: ITDR solutions continuously monitor identity activities for signs of malicious behavior, including unusual login attempts, anomalous access patterns, and unauthorized use of privileged accounts.
- Pre-emptive enforcement and incident response: When a threat is detected, ITDR systems can automatically trigger response actions in real time, such as alerting security teams, locking compromised accounts, and enforcing additional authentication requirements.
- Identity threat visibility: ITDR provides comprehensive visibility into identity-related activities across all systems, including on-prem and cloud environments. This visibility is crucial for identifying potential vulnerabilities and understanding the scope of an attack.
- Behavioral analytics: By analyzing user behavior, ITDR solutions can establish a baseline of normal activities and detect deviations that may indicate a security threat. This proactive approach helps in identifying sophisticated attacks that might bypass traditional security measures.
Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM)
Identity Security Posture Management (ISPM) involves continuously assessing and improving the security posture of an organization’s identity infrastructure. It encompasses practices such as regular security assessments, vulnerability management, and policy enforcement to ensure that identity security measures remain effective over time.
At its core, ISPM involves a comprehensive set of practices designed to maintain the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of sensitive identity-related data. These practices include:
- Regular security assessments
- Vulnerability management
- Policy enforcement
- Identity governance
- Continuous monitoring
- Incident response
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security mechanism that requires users to provide two or more forms of verification before accessing an account, application, or system. It adds a critical layer of protection beyond just a username and password and is a key tenet of identity security. MFA uses a combination of the following factors:
- Something you know – like a password or PIN.
- Something you have – such as a smartphone, security token, or smart card.
- Something you are – biometric identifiers like fingerprints, facial recognition, or retina scans.
A login attempt must meet at least two of these factors to be successful.
Cyberattacks such as phishing, credential stuffing, and brute-force attacks can easily compromise single-factor authentication. MFA significantly reduces this risk.
- Stronger access control – Prevents unauthorized logins, even if credentials are stolen.
- Reduced attack surface – Adds friction for attackers trying to move laterally across systems.
- Regulatory compliance – Supports adherence to security frameworks (e.g., NIST, GDPR, HIPAA).
- Improved user confidence – Builds trust by showing a commitment to security.
Implementing MFA is one of the most effective ways to secure digital identities and protect sensitive data. It’s a low-cost, high-impact control that’s essential in today’s threat landscape.
Privileged Access Security
Privileged Access Security (PAS) is a modern identity security approach designed to protect the most sensitive identities—like admins, service accounts, and IT personnel—against advanced threats. Unlike traditional Privileged Access Management (PAM), PAS focuses on securing privileged users, not just managing them.
PAS enforces advanced identity controls in real time across hybrid environments, without relying on vaulting or agent deployments. By moving away from the traditional approach of vaulting, businesses can protect their privileged accounts without enduring the lengthy, complex onboarding process associated with PAM.
Key security capabilities include:
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Access – Grants temporary, time-bound access only when needed.
- Tiering – Segregates access levels to limit high-risk lateral movement.
- Virtual Fencing – Dynamically enforces boundaries between users, resources, and environments.
This proactive approach ensures privileged identities can only access what they’re authorized to, when and where it’s truly necessary.
Authentication Firewall
An Authentication Firewall is a security control that monitors and governs authentication traffic across an organization’s digital environment. Instead of relying solely on access decisions made after authentication, this approach introduces policy enforcement at the point of authentication itself—evaluating login attempts before a user, application, or system is granted access.
- Real-time inspection of authentication attempts across all protocols (e.g., Kerberos, NTLM, RADIUS, SAML).
- Policy-based access decisions informed by risk, context, identity, and behavior.
- Protocol-agnostic enforcement that works across hybrid and legacy environments.
- Blocking or redirecting suspicious logins before access is established.
- No reliance on endpoint agents or application-level integrations.
Authentication is often the first and most vulnerable step in the attack chain. Threats like credential stuffing, lateral movement, and privilege escalation frequently exploit weaknesses in the authentication layer. An Authentication Firewall helps neutralize these risks at their source, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers and enabling Zero Trust enforcement across the enterprise.
AI Agent Security
AI Agent Security refers to identity and access governance for autonomous systems, such as agents powered by large language models (LLMs) or AI-driven orchestration platforms. These agents can initiate actions independently—such as modifying systems, generating content, or accessing data—and therefore require identity-level controls similar to those used for human users.
- Identity and behavioral monitoring for AI agents and automated workflows.
- Policy enforcement based on agent role, context, and intent.
- Visibility into agent actions, including access to systems, data, and other resources.
- Limitations on agent permissions, with dynamic restriction of sensitive tasks.
- Audit trails to ensure accountability and compliance.
AI agents are rapidly becoming operational in enterprise environments. As they gain access to sensitive data and critical infrastructure, they pose unique risks, such as acting on poisoned inputs, making unauthorized decisions, or being repurposed by attackers. Securing these agents with structured identity controls is essential to preventing unintended or malicious outcomes and increasing resilience to identity-based threats.
Non-Human Identity (NHI) Security
Non-Human Identity (NHI) Security is the practice of securing machine identities that interact with enterprise systems, such as service accounts, APIs, scripts, bots, and cloud functions. These identities often operate without human oversight and have persistent access to critical resources.
- Continuous discovery and classification of NHIs across cloud and on-prem environments.
- Behavioral baselining and anomaly detection for NHI activity.
- Context-aware access controls that adapt to changes in risk or usage patterns.
- Policy enforcement without relying solely on credential vaulting or rotation.
- Visibility and auditability of non-human interactions with sensitive systems.
NHIs vastly outnumber human identities in most organizations and are often under-managed and over-permissioned. They represent a major blind spot for identity and access management programs, and attackers frequently exploit NHIs to maintain persistence, escalate privileges, or exfiltrate data. Securing these identities is crucial for reducing organizational risk, especially in automated and cloud-native environments.
Final Word: Identity is the New Perimeter
Today’s cybersecurity battlefield is identity-first. But with the right tools, the right mindset, and the IDEAL identity security strategy, you can protect every identity, everywhere, all at once. To learn more about taking your identity security to the next level, get in touch with Silverfort today. Or why not check out our library of identity security resources—from free tools to the latest threat intel.