Stop attacks from spreading in real time.
Defend against ransomware attacks and put a stop to lateral movement by detecting and blocking malicious authentications as they happen.
The identity way is the only way.
Silverfort is the only solution that can enforce MFA at scale in any environment to disable lateral movement and ransomware spread.
MFA without limits
Block ransomware from spreading through your network using compromised credentials by placing MFA policies on PsExec, PowerShell, WMI and more.
Prevention—not just detection
MFA outsources the initial response to the entire workforce, engaging the security team only in true positive where compromised has been validated by the user.
Privileged access protection
All admins, including both human users and service accounts are protected with automated least-privileged access policy to minimize compromise impact and prevent malicious abuse of their access privileges.
The Silverfort Identity Security Platform
How it works
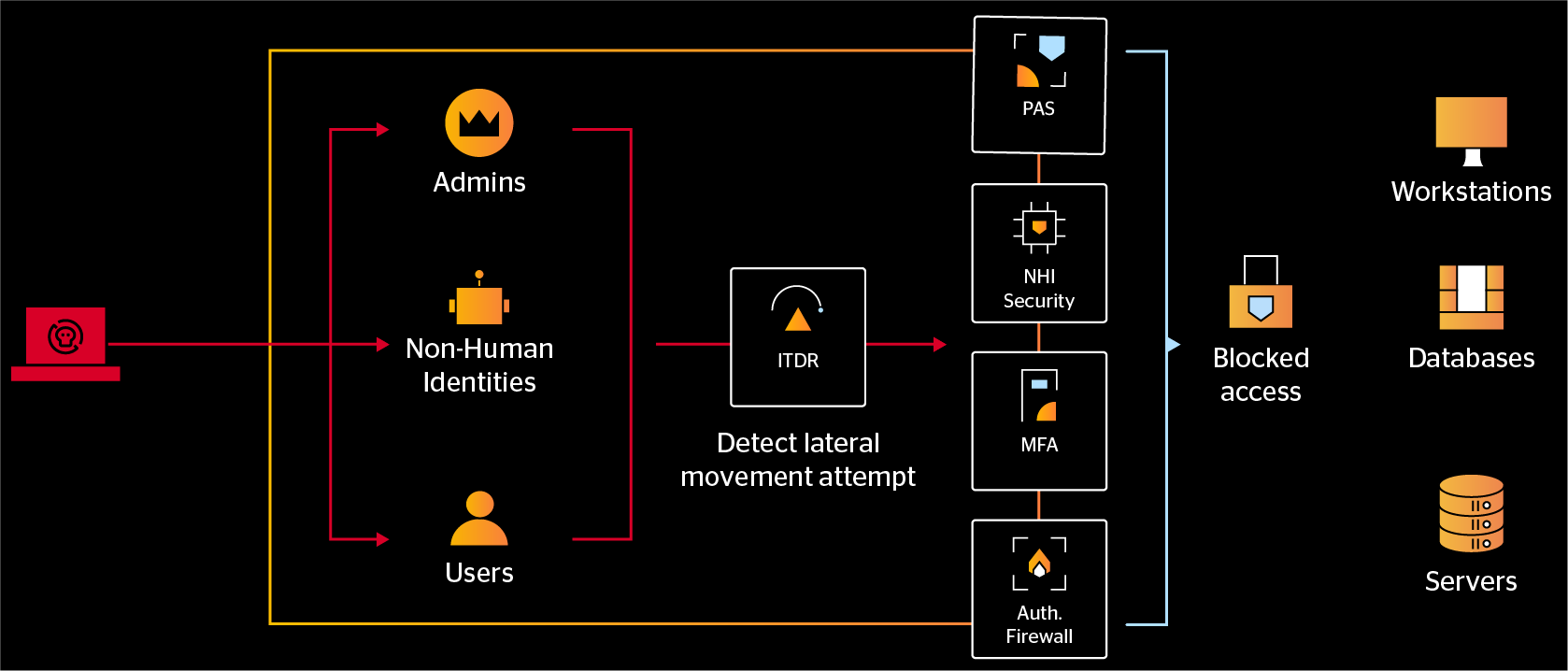
Automate protection with real-time access controls.
Detect with accuracy
Our platform analyzes every authentication and access attempt to detect the use of malicious TTPs for privilege escalation or lateral movement.
Protect with confidence
Configure MFA policies to trigger protection for detected risks, disabling adversaries from using compromised credentials for malicious access.
Secure service accounts
Enforce automated access policies on your service accounts to ensure they cannot access any resources outside of their designated scope.
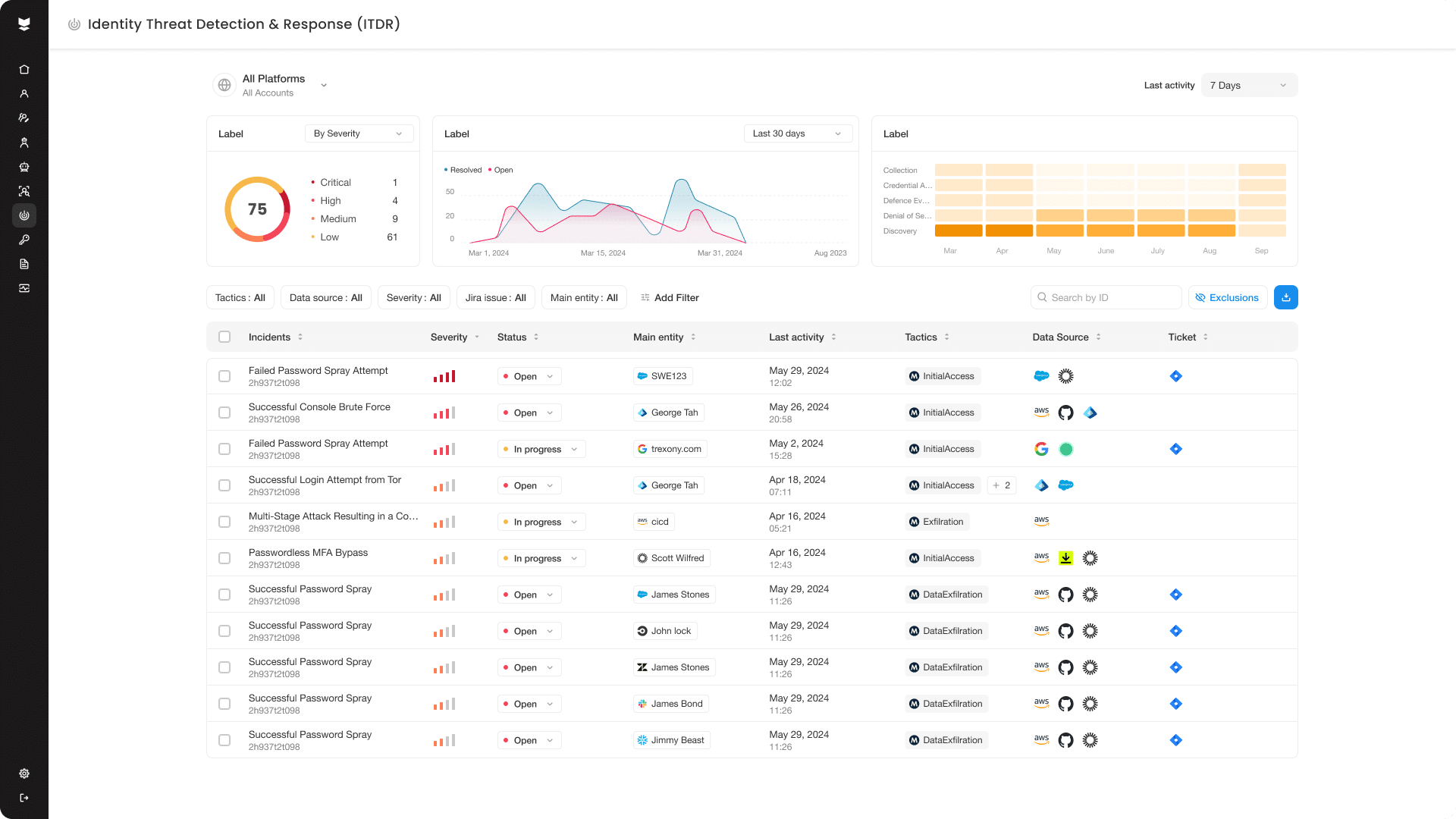

We dared to push identity security further.
Discover what’s possible.
Set up a demo to see the Silverfort Identity Security Platform in action.