Applying security controls across an organization’s environment must be a top priority for every organization, regardless of its size, sector, or maturity. To help guide organizations in managing and reducing their cybersecurity risks, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) created a security framework that provides guidelines for organizations to manage and mitigate cybersecurity risks.
In this article, you will learn about the latest version of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 version and how Silverfort can help organizations get aligned with its identity security aspects.
What is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0 was originally released in 2014 by the National Institute of Standards and Technology. The framework addresses a set of principles and best practices for organizations especially from the industrial and government sector. NIST 2.0 framework consists of 6 key core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover and Govern. These core functions are essential for all organization’s approach to managing cybersecurity risks. These functions are designed to be implemented continuously and dynamically, providing a strategic view of how an organization manages its cybersecurity risks.
Let’s focus on the identity security aspect of NIST CSF 2.0.
The Identity Security Aspects of the NIST CSF 2.0
With the identity attack landscape continuously evolving, organizations have become increasingly concerned about their identity security. Through the compromise of user credentials, attackers are gaining malicious access to critical resources which allows them to conduct lateral movement and ransomware attacks. To address the importance of identity security, NIST CSF 2.0 provides the following guidelines to organizations:
Asset Management (ID.AM)
Organizations must identify and manage all their assets, including data, software, hardware, systems and people, based on their importance to business objectives and risk management strategy:
- Organizations should manage and maintain all types of users including human, machine-to-machine and non-human identities
- Organizations should maintain all user authentication activity in their environment and detect who is accessing which resources as well as what authentication protocols are being used
Risk Assessment (ID.RA)
Organizations must understand all the cybersecurity risks that might affect its environment, including all assets and users:
- Organizations should identify and record all the internal and external threats as well as vulnerabilities that can be potentially exploited
- All the potential security risks must be prioritized including inherent risks
Identity Management, Authentication, and Access Control (PR.AA)
To minimize risk of unauthorized access, only identified users can get an access to physical and logical assets of the organization:
- Organizations should manage all the identities and credentials for authorized users, services and on-prem resources
- All the authentications in the organization’s environment are made by identified users and services, including service accounts
- Organizations should define and manage security policies for user access permissions and authorizations in accordance with the principle of the least privilege
Continuous Monitoring (DE.CM)
Organizations should implement continuous monitoring activities to detect anomalies and any potentially adverse events, including:
- User activity and authentication
- Access logs to resources
- Third-party user activities
Incident Analysis (RS.AN) and Mitigation (RS.MI)
To minimize the effects of the incidents and ensure effective response, organizations should investigate all the incidents and imply recovery activities:
- Organizations should analyze the root cause of any security incident to gain full visibility into the attack flow and its consequences
- Organizations should contain and eradicate all security incidents
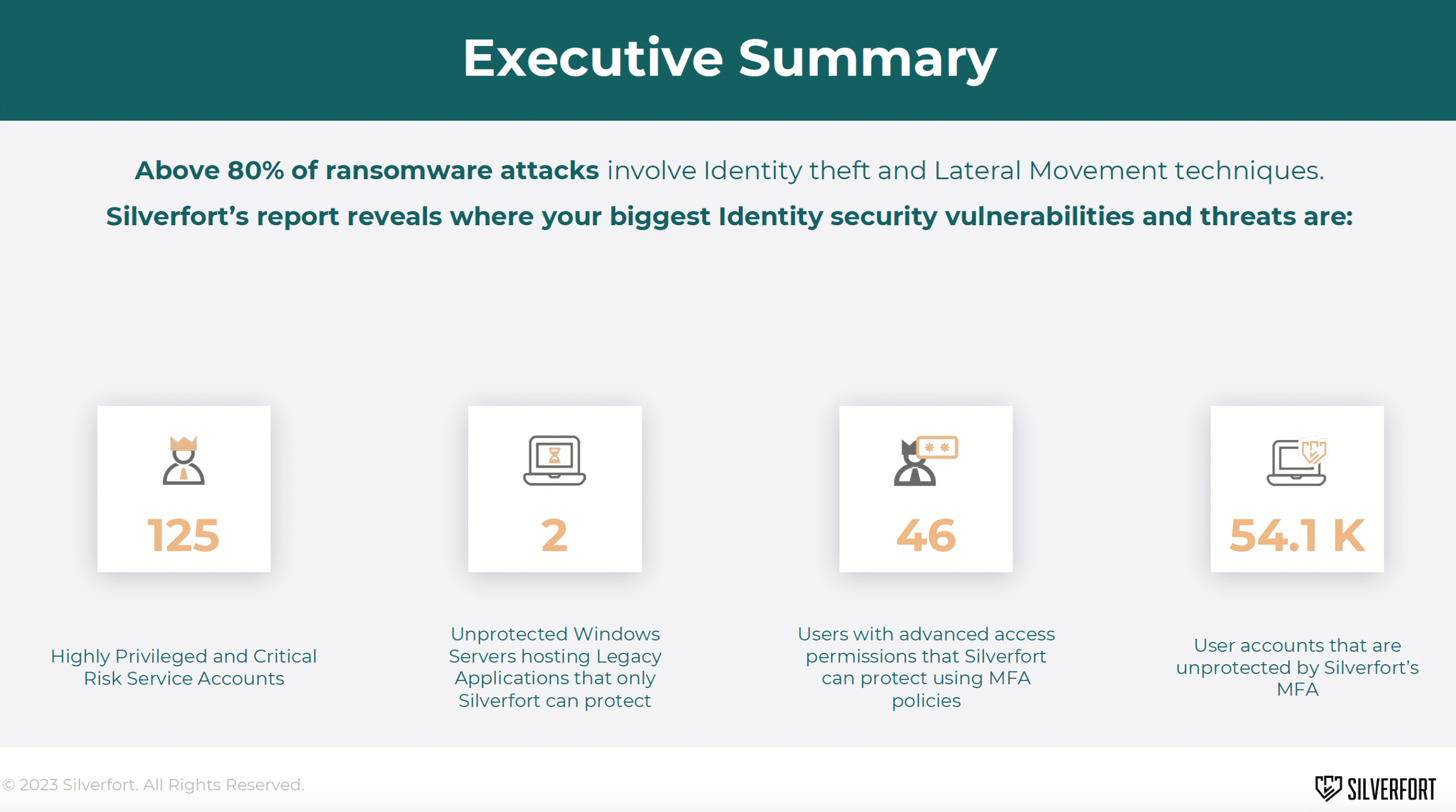
Getting NIST 2.0 Compliant with Silverfort
1. Asset Management (ID.AM)
With Silverfort you are provided with an in-depth identity inventory that displays the types of users and resources in your environment as well as weaknesses in your security. With continuous visibility and actionable insights into everything identity-related, Silverfort allows you to take a more proactive approach to your identity security posture management with just a few clicks.

2. Risk Assessment (ID.RA)
Silverfort’s risk assessment provides a comprehensive overview of the of an organization’s identity security posture. It includes real-time visibility into all access attempts across your environments and runs a real-time risk analysis to calculate the risk score of each user authentication request. If any unauthorized or abnormal behavior is identified, the system can take immediate action, such as terminating the session or requesting additional authentication.
The risk assessment also uncovers any security hygiene issues that can expose the environment to identity threats while detecting any active ones already underway. With this information in hand, organizations can easily identity the identity security gaps that need to be mitigated to align with NIST’s risk assessment requirements.
3. Continuous Monitoring (DE.CM)
Silverfort provides centralized visibility into every authentication and access request across all users and resources in the hybrid environment, thanks to its native integrations with all identity providers. Silverfort’s analysis engine can determine the risk of every authentication, so organizations can detect and respond to any potential security threats in real time – including blocking the access of any accounts that display anomaly behavior.
4. Identity Management, Authentication, and Access Control (PR.AA)
Silverfort enables organizations to enforce user access policies in real-time, so only authorized users and devices can gain access to the resources they are assigned to. By applying Silverfort access policies organizations can apply flexible policies that enforce security controls across their user base which can be defined by specific user roles, risk indicators, and organizational security policies.
As a result of these policies, alerting, MFA, or blocking access to all the users who were defined in the policy can be enforced. Silverfort can block access requests for every type of user, service account, access method, and resource in real-time, effectively halting any authorized access from occurring.

5. Incident Analysis (RS.AN) and Mitigation (RS.MI)
All authentication and access attempts are monitored and analyzed continuously by Silverfort, including the source, destination, risk level, and much more. In addition, you can apply access policies, either by yourself or by Silverfort, that will notify you when an access attempt deviates from normal behavior and/or deny access. Silverfort can assist you in containing, investigating, and recovering compromised accounts if you experience a security incident.
Want to learn more about how Silverfort can help you address the identity security aspects of NIST CSF 2.0? Schedule a call with one of our experts or fill out this form for a pricing quote.

